Overview
This project focused on a comparative analysis of the physical properties of the nebular structure around NGC 7293 (the Helix Nebula) using data from the IRIS and AKARI all-sky infrared surveys. The aim was to determine whether the region shows evidence of active star formation or remains in local thermodynamic equilibrium.
Key Objectives
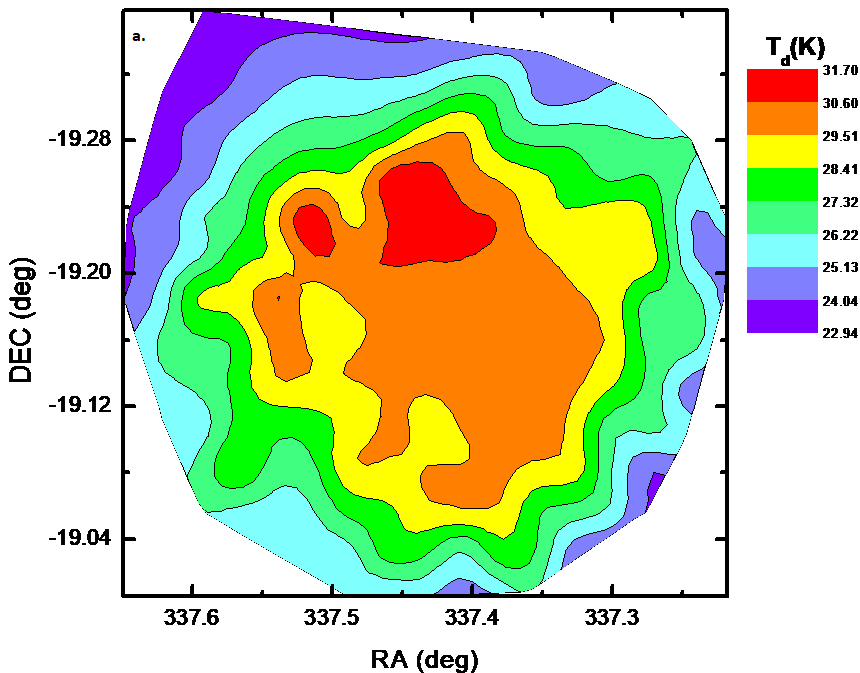
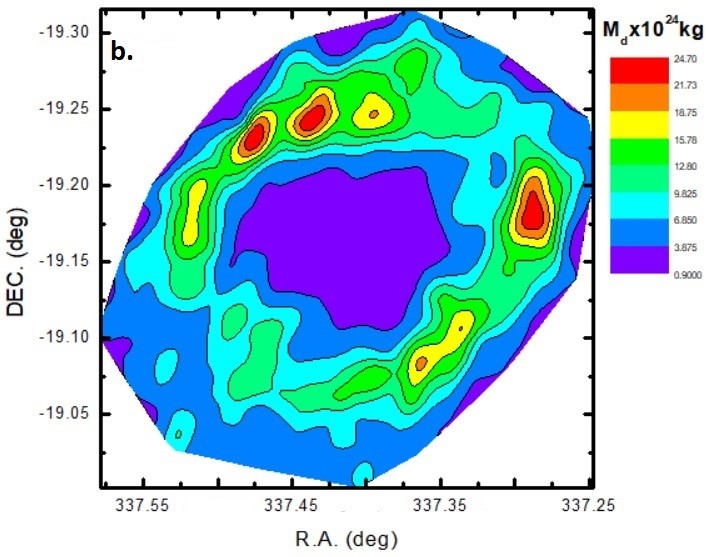
- Analyze temperature and mass distribution using infrared data at various wavelengths (60, 90, 100, and 140 µm).
- Estimate dust color temperatures, masses, and Jeans mass from IRIS and AKARI maps.
- Assess thermodynamic stability and star formation potential of the nebula.
Data & Tools
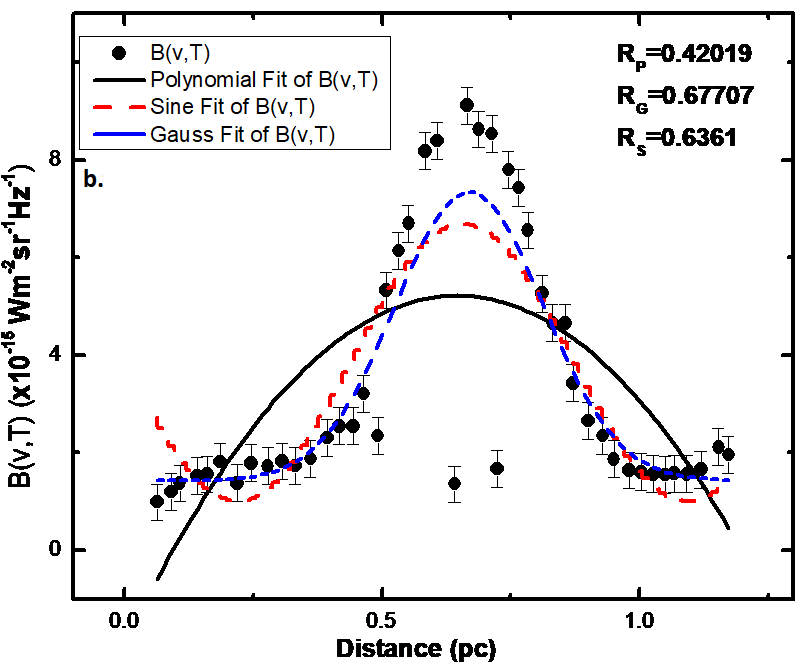
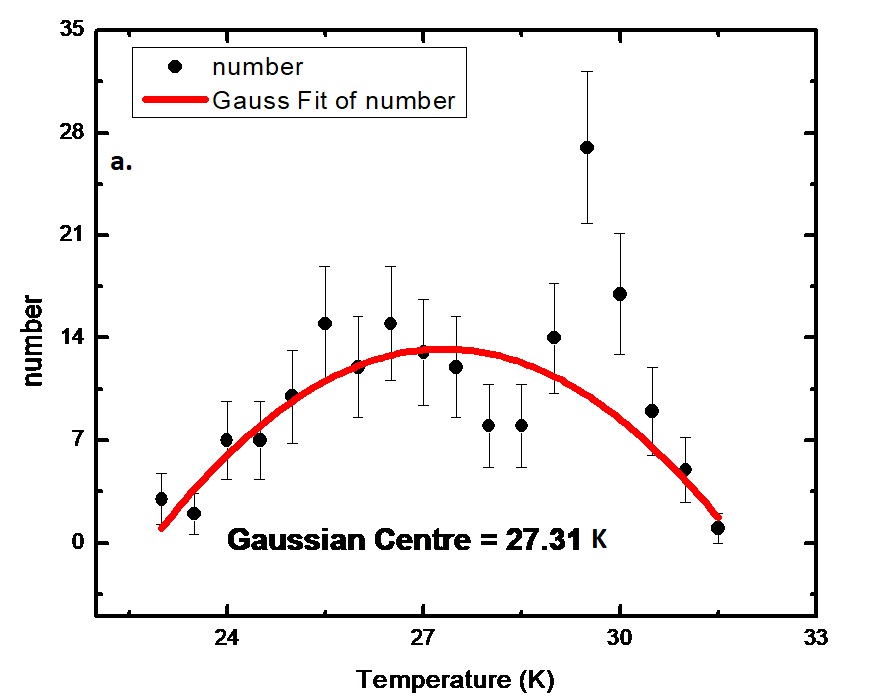
FITS images were obtained via the SkyView Virtual Observatory and processed using Aladin v2.503. Temperature and mass maps were derived by applying Planck’s function and dust emission models. Gaussian and regression analyses helped confirm local equilibrium conditions.
Findings
- The structure showed distinct flux peaks across all bands, more clearly defined in the AKARI maps.
- Average temperatures: ~31 K (IRIS) and ~22 K (AKARI).
- Total dust mass: ~6.5 × 10²⁶ kg (IRIS), ~3.0 × 10²⁸ kg (AKARI).
- Estimated Jeans mass in both maps was significantly higher than actual mass, implying no active star formation.
Figures
Note
This work was completed as part of my undergraduate thesis at Sainik Awasiya Mahavidyalaya, Tribhuvan University, and presented in partial fulfilment of the B.Sc. in Physics. Tools used include Aladin, Origin, Excel, and IR image processing techniques. This work was also presented at ANPA conference 2020.
Keywords
NGC 7293, Helix Nebula, IRIS, AKARI, infrared astronomy, dust temperature, Jeans mass